Best Practices - Data Publishing
OAIS (in more detail Figure 4-1: OAIS Functional Entities, Figure A-1: Composite of Functional Entities and Figure 4-16: Preservation Description Information) is a reference model for Open Archival Information System. In the context of Best Practices - Data Publishing the OAIS terminology and Functional Entities are labelled green.
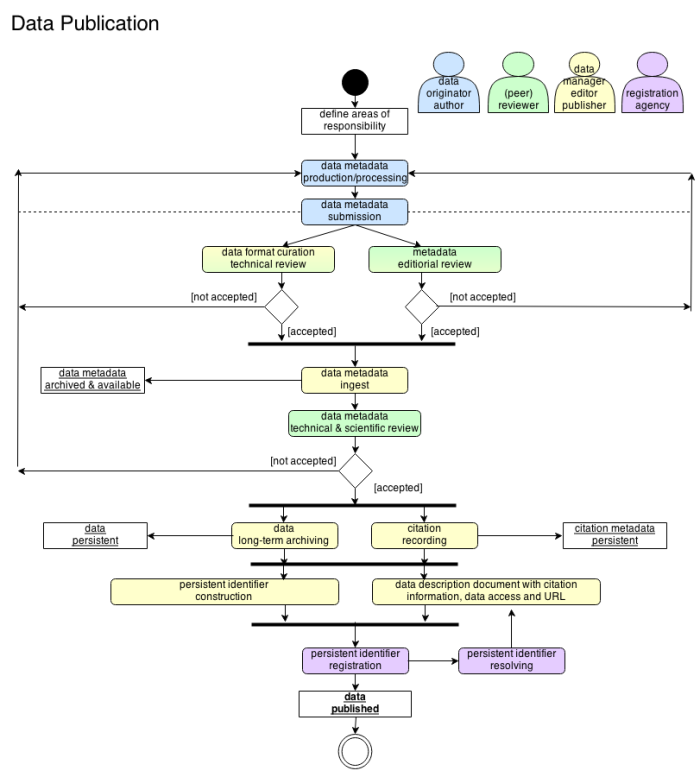
Roles
data originator/producer, author: data and metadata creator with assertions about trustworthiness, reliability of data
reviewer: responsible for quality assurance of data and metadata with review criteria publisher predefined or community accepted.
data manager: responsible for
data staging
long-term archiving of data and metadata
curation - computer readable and human interpretable data and metadata, DDD (Data Description Document)
resolving of persistent identifier – useable to find the data and metadata
identifiermanagement
access activities - gatekeeper
editor/publisher: editorial functions including assembly and definition for the dataset metadata with assertions about trustworthiness, reliability of data and review controlling. Responsible for persistent identifier construction and citation recording.
registration agency: responsible for registration of persistent identifier and citation metadata.
Activities
data production processing: get information about data production processing here.
data submission: submission of the Submission Information Package (SIP) equal to uml acitivity data and metadata submission. Get information about data submission, go to the page create and manage data and submit data. The administration negotiates the submission agreements.
data staging: it belongs to the format curation and archive requirements. The administration establishes the standards and policies.
Subactions
- data format curation
- technical review - quality assurance
- metadata editiorial review- quality assurance
- data metadata ingest with generation of Archival Information Package (AIP) and archival storage. AIP is a combination of SIP, QA results and Data Management Reports.
review technical and scientific: aspect are consistency / integrity, completeness, accessibility, provenance, accuracy / evaluation.
data long-term archiving-preservation: it belongs to the format curation and archive requirements.
allocate data PID: get information about PID allocation, go to the page register data. The PID belongs to the Preservation Description Information (PID) reference.
Subactions
- persistent identifier construction
- citation recording
- provide for each PID a data description document with citation information, data access with Dissemination Information Package (DIP) and URL. The DIP is derived from the AIPs and sent to the Consumers.
- persistent identifier registration
- persistent identifier resolving
data submission: get more information about data submission at WDCC here.
data staging:
Subactions
- data format curation: assembly and definition of format e.g. netcdf and grib as tar files
- technical review: aspects are file names, file extensions, file formats, checks of versioning according to conceptional development of work flow, file size checks and checksum
- metadata editiorial review: aspects are metadata of standard components with check documentation, consistency of formal CV and access constraints handling
- data metadata ingest into CERA and ESGF DKRZ Nodes
review technical and scientific: aspect are consistency / integrity, completeness, accessibility, provenance, accuracy / evaluation. The assistent system Atarrabi provides a key part of the review process by supporting the authors and reviewer final quality assurance of data and metadata.
CERA data long-term archiving
allocate data PID:
Subactions
- persistent identifier construction: Prefix=10.1594 and Suffix=/WDCC/<entry_acronym> e.g. 10.1594/WDCC/CLM_A1B_2_D2
- citation recording: (person(s) or institute(s) responsible for this assemblage of data: e.g. author, data collector, editor...) for example
- data description document with citation information, data access and URL: examples compact page and CMIP5
- persistent identifier registration with the DOI System and DataCite
- persistent identifier resolving: IDF resolver e.g. http://dx.doi.org/DOI:10.1594/WDCC/CLM_A1B_2_D2